Can Diet Help Improve Sleep Apnea Symptoms?

Sleep apnea is often treated with devices like CPAP or custom oral appliances—but could something as simple as what you eat also make a difference?
The answer is yes. While diet won’t replace medical treatment, research shows that targeted nutrition and healthy lifestyle changes can reduce the severity of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and support better breathing during sleep.
Let’s explore the connection between food and sleep apnea—and what changes might help you sleep more soundly.
Understanding the Diet–Sleep Apnea Connection
Obstructive sleep apnea happens when the muscles around your throat relax too much during sleep, leading to partial or complete airway collapse. This disrupts your breathing, causes fragmented sleep, and increases your risk for serious health issues—like high blood pressure, heart disease, and cognitive decline.
Diet can play a role in OSA in two key ways:
- Weight Management
Extra tissue around the neck and upper airway increases the likelihood of obstruction at night. Even a 10% weight loss can significantly improve symptoms in overweight individuals. - Inflammation and Fluid Retention
Certain foods can worsen inflammation and fluid buildup in the upper airway, making it harder to breathe at night.
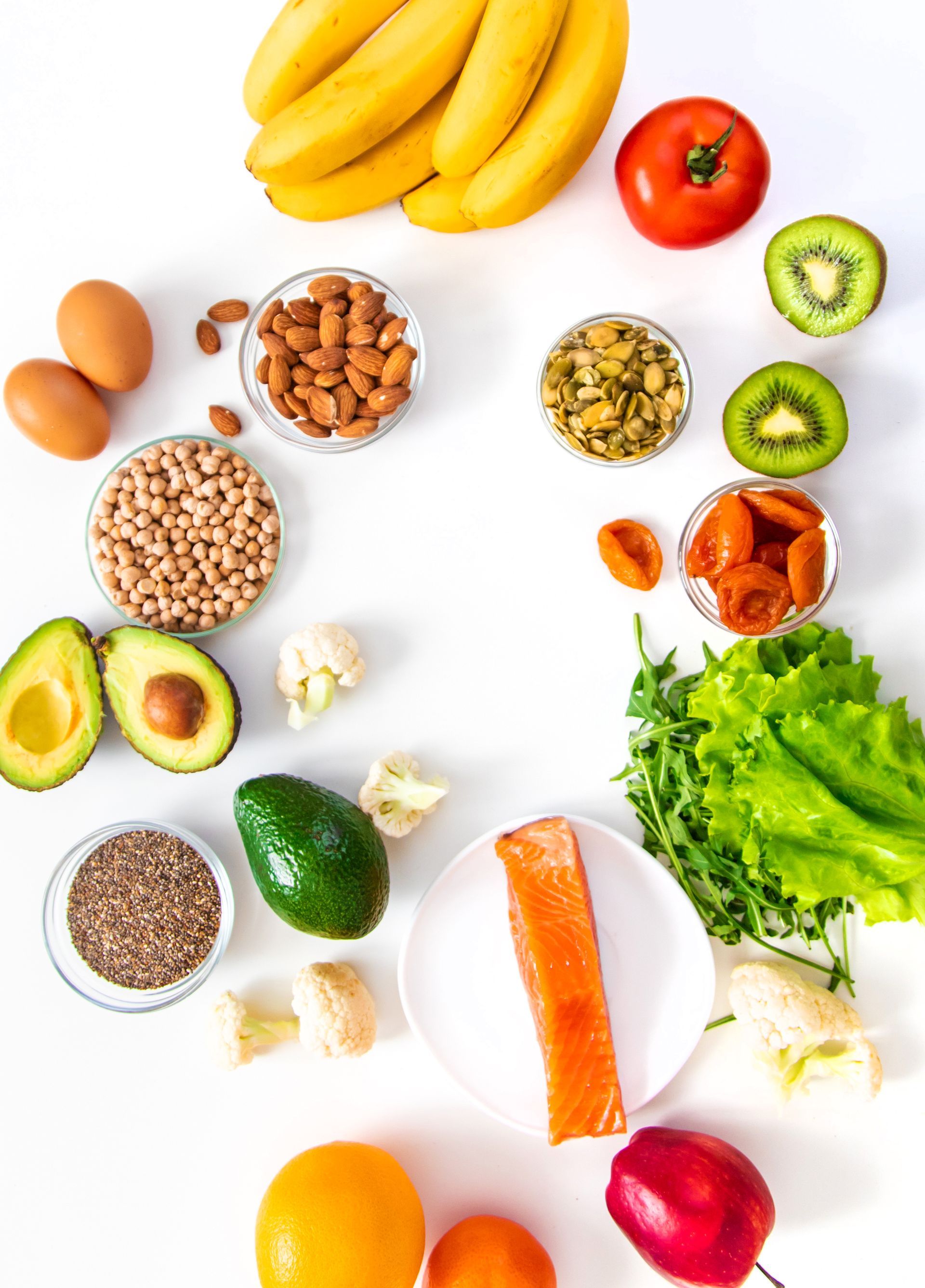
Foods That May Help With Sleep Apnea Symptoms
1. Anti-Inflammatory Foods
Reducing systemic inflammation can ease airway swelling.
Eat more of:
- Leafy greens, berries, turmeric, ginger
- Fatty fish like salmon or sardines (rich in omega-3s)
- Nuts and seeds
2. Whole Foods & Fiber
A diet high in fiber and low in processed foods helps regulate weight and reduces oxidative stress.
Choose:
- Oats, quinoa, lentils
- Fresh fruits and vegetables
- Beans and legumes
3. Mediterranean-Style Diet
Multiple studies show that a Mediterranean diet—rich in vegetables, olive oil, lean proteins, and whole grains—can reduce the severity of OSA, especially when paired with weight loss.
Foods to Limit or Avoid
1. Processed and High-Fat Foods
Heavy, greasy meals can increase inflammation and cause weight gain.
- Fried foods
- Processed meats
- High-fat dairy
2. Alcohol
Alcohol relaxes the muscles of the throat and can make apnea episodes more frequent and severe—especially before bed.
3. Sugary Foods and Refined Carbs
These cause blood sugar spikes and can worsen overnight inflammation and fluid retention.
Eating large meals late at night can:
- Increase reflux (which worsens OSA)
- Disrupt digestion
- Lead to poor sleep quality
What About Meal Timing?
Eating large meals late at night can:
- Increase reflux (which worsens OSA)
- Disrupt digestion
- Lead to poor sleep quality
Tip: Try to finish eating at least 2–3 hours before bedtime.
Bonus Tip: Hydration Matters
Mucus buildup in the airway is more likely when you're dehydrated. Drinking enough water throughout the day (but not too much right before bed) can help keep airways clearer.